Characteristics of Chroamor
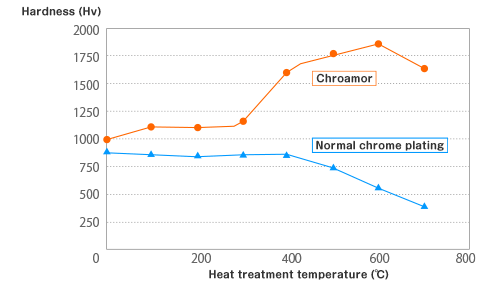
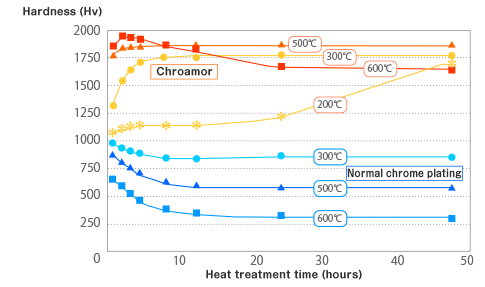
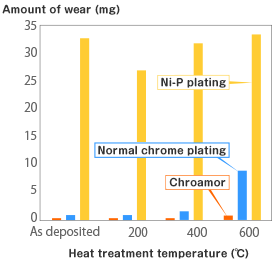
Relationship between heat treatment
and the amount of wear
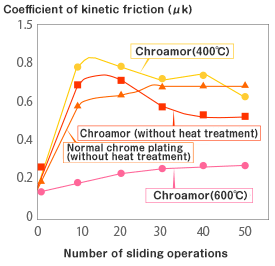
Differences in coefficient of kinetic friction between hard chrome plating and Chroamor
Cross section of
Chroamor film
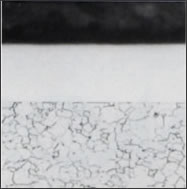
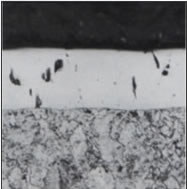
Cross section of
hard chrome plating film
Chroamor allows low-temperature treatment compared to diffusion treatments such as carburizing, nitriding, and boride methods, or dry surface hardening methods based on chemical or physical vapor deposition, which means that Chroamor imposes less thermal influence on materials.
Chroamor can be detached and replated in the same way as normal chrome plating.
Chroamor is a high-hardness plating, thus causing macrocracks to occur when the plating thickness exceeds 5 μm. However, thanks to the excellent characteristics described above, Chroamor provides sufficient functionality even if its thickness is a fraction of the thickness of normal chrome plating.
Materials that can be plated
Uses of Chroamor
| Semiconductor-related parts | Various sealing molds, various pins (such as ejector pins, movable pins, pilot pins, guide pins, and core pins), various punches (such as bending punches, forming punches, hole punches, and cutting punches), various dies (such as bending dies and forming dies), various plates (such as guide plates, feed plates, and heater plates), various blocks (such as center blocks, cull blocks, heater blocks, and guide blocks), cavities, plungers, etc. |
| Parts for molding resin | T-shaped dies, clasps, screws, collars, adjusting rings, lips, pipes, mandrels, nipples, nozzles, sleeves, various molds, adapters, plates, guides, etc. |
| Parts for molding glass | Annealing screws, guides, forming rollers, pushers, chutes, various molds, etc. |
| Spinning machine parts | Clasps, various guides, reed blades, perforated sheets, hot rollers, guides, rollers, etc. |
| Wear-resistant parts | Cams, shafts, rolls, guides, blades, pulleys, pistons, various pins, plates, etc. |
| Machined metal parts | Bending dies, drawing dies, forming rolls, punches,guides, dies, rollers, etc. |
| Other various corrosion-resistant parts, heat-resistant parts, printing machine parts, food manufacturing related parts, precision parts, parts molded by die casting, pharmaceutical manufacturing related parts, logistics machinery parts, etc. | |
Glass forming molds are often heated at high temperature (600 to 700℃) and so if normal chrome plating is applied, it cannot be used for a long period due to problems such as the occurrence of hairline cracks, the peel-off and transfer of oxide films formed on the surfaces, and their resultant abrasion. However, using Chroamor forms fine and rigid oxide films through heat treatment, making the peel-off of oxide films extremely little and retaining their rigidity at high temperature, making it possible to extend the service life of the product and reduce the maintenance burden.
Most metal powder, ceramic powder, and other powder used with powder injection molding are very hard materials, causing significant wear on molded parts and affecting the working environment due to dust produced by abrasion. Applying Chroamor to die plates has been producing satisfactory results. For example, a die plate had severe wear with a maximum depth of 0.7 mm when approximately 700,000 shots were delivered, but the same die plate to which Chroamor was applied had almost no wear even after 3,000,000 shots were delivered.
| Otec’s functional plating film | Reference plating film | ||||
| Type | CHROAMOR | Chrome plating | TFE-LOK | Electroless nickel plating Ni-P |
|
| Plating method | Electroplating | Electroplating | Chrome plating Chemical treatment Mechanical treatment | Electroless plating | |
| Film structure | Cr-C amorphous material |
Cr crystalline material |
Cr+PTFE composite film |
Ni-P amorphous material |
|
| Glossiness | ◎ | ○ | △ | △ | |
| Thickness uniformity | △ | △ | △ | ◎ | |
| Corrosion resistance | ○ | △ | △ | ◎ | |
| Wear resistance | ◎ | ○ | ○ | △ | |
| Heat resistance | ◎ | ○ | △ | ○ | |
| Hardness (Heat treatment temperature) |
As deposited | Around Hv1,000 | Around Hv900 | Around Hv850 |
Around Hv500 |
| 400℃ | Around Hv1,700 | Around Hv850 | - | Around Hv950 | |
| 600℃ | Around Hv1,800 | Around Hv600 | - | Around Hv650 | |
| Self-lubricating capabilities | As deposited:○ | △ | ◎ | △ | |
| 600°C heat treatment:◎ | |||||
| Non-adhesiveness | As deposited:△ | △ | ◎ | △ | |
| 600°C heat treatment:○ | |||||
 |
 |
| Pins | Screw |









